Understanding Dengue Fever Treatment: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction:
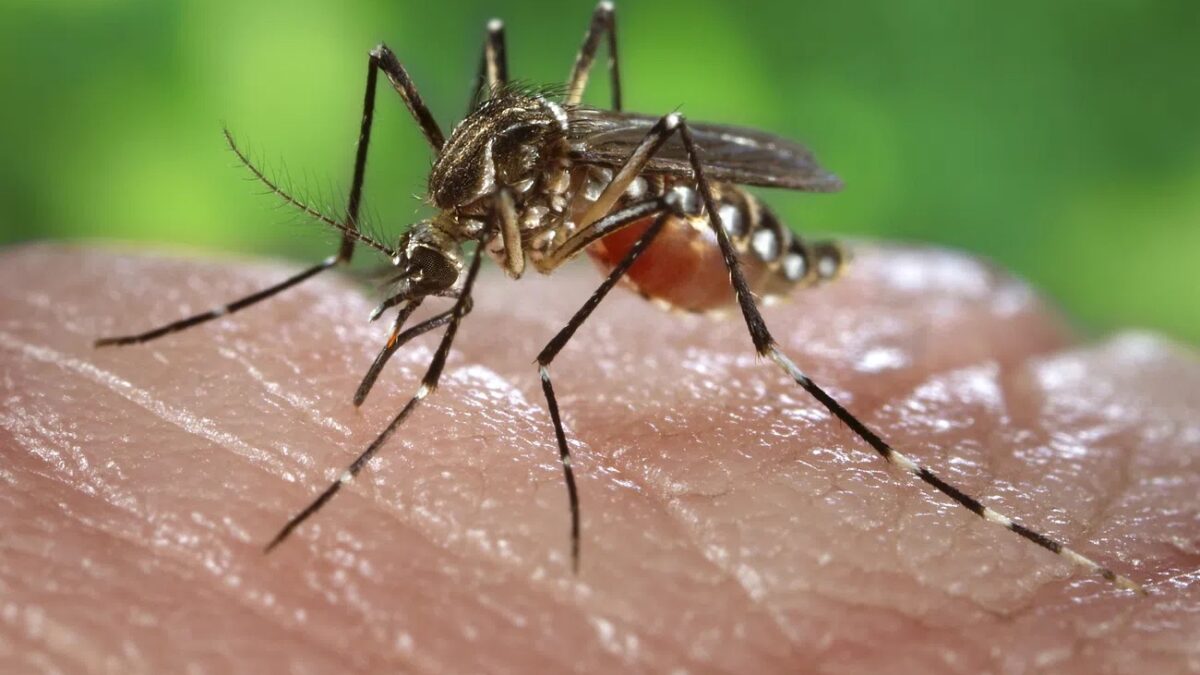
Dengue fever, a mosquito-borne viral infection, poses a significant public health concern in tropical and subtropical regions around the world. Characterized by flu-like symptoms, dengue fever can range from mild to severe, with potentially life-threatening complications. While prevention through mosquito control measures remains crucial, understanding the available treatments is equally important. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various aspects of dengue fever treatment, from supportive care to potential future interventions.
Early Detection and Diagnosis:
Timely diagnosis is paramount in the effective management of dengue fever. Health professionals typically rely on clinical assessments, supported by laboratory tests such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) or serological tests. Early detection allows for prompt initiation of appropriate treatment, reducing the risk of complications
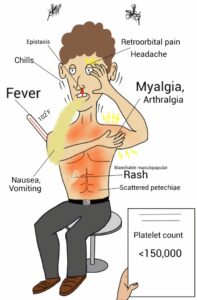
Dengue Fever Treatment
Supportive Care:
As there is no specific antiviral medication for Dengue Fever Treatment, treatment primarily involves supportive care to alleviate symptoms and manage complications. Key components of supportive care include:
- Hydration: Adequate fluid intake is crucial to prevent dehydration, especially in cases of severe dengue (dengue hemorrhagic fever or dengue shock syndrome). Intravenous fluid replacement may be necessary for patients unable to maintain oral intake.
- Pain Management: Pain relievers such as acetaminophen (paracetamol) are commonly used to alleviate fever and discomfort. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), including aspirin and ibuprofen, should be avoided as they can increase the risk of bleeding.
- Rest: Adequate rest is essential for the body to recover from the infection. Patients are advised to take it easy and refrain from strenuous activities during the recovery period.
Monitoring and Hospitalization:
Close monitoring of vital signs, platelet counts, and hematocrit levels is crucial, especially in severe cases. Hospitalization may be required for individuals experiencing severe dengue symptoms or complications. Monitoring allows healthcare providers to intervene promptly if there are signs of worsening symptoms or the development of severe dengue.
Platelet Transfusion:
In severe cases of dengue fever, a significant decrease in platelet count may occur, leading to a condition known as thrombocytopenia. In such instances, platelet transfusions may be necessary to prevent or manage bleeding complications. However, platelet transfusions are typically reserved for cases with significant bleeding or a very low platelet count.
Preventing Mosquito Bites:
While not a direct treatment for the infection, preventing further mosquito bites is crucial to avoid the transmission of the virus to others and to prevent secondary infections. Patients recovering from dengue fever should continue to use mosquito repellents, wear protective clothing, and sleep under bed nets to reduce the risk of additional mosquito bites.
Avoiding Certain Medications:
Patients with dengue fever are advised to avoid medications that can increase the risk of bleeding. As mentioned earlier, NSAIDs should be avoided due to their anticoagulant effects. Aspirin, in particular, should be avoided as it can contribute to bleeding complications.
Immune System Support:
While there is no specific antiviral treatment for dengue, supporting the immune system is crucial for recovery. A nutritious diet, including foods rich in vitamins and minerals, can help bolster the immune response. Supplements may be recommended if nutritional deficiencies are identified.
Experimental Treatments and Ongoing Research:
The search for specific antiviral treatments for dengue fever is ongoing, and various experimental approaches are being explored. Some potential interventions include antiviral drugs, monoclonal antibodies, and vaccines. However, these treatments are still in the experimental stages, and further research is needed to determine their efficacy and safety.
Preventive Measures for Severe Dengue:
Preventing the progression to severe dengue is a crucial aspect of treatment. Recognizing warning signs, such as persistent vomiting, severe abdominal pain, bleeding, and rapid breathing, is essential. Seeking prompt medical attention when these signs emerge allows healthcare professionals to intervene and provide the necessary care to prevent complications.
Post-Recovery Follow-Up:
Even after the acute phase of dengue fever has passed, individuals are advised to undergo regular follow-up with healthcare providers. This is particularly important for monitoring any lingering symptoms and ensuring that the individual has fully recovered. Additionally, monitoring for potential complications, such as prolonged fatigue or clotting disorders, is essential.
Conclusion:
Dengue fever treatment primarily involves supportive care to manage symptoms, prevent complications, and promote recovery. Early detection and prompt medical attention are crucial in preventing the progression to severe dengue. While ongoing research explores potential antiviral treatments and preventive measures, the current focus remains on effective supportive care.
Public health efforts also play a pivotal role in dengue fever management, including mosquito control measures to reduce the transmission of the virus. As we navigate the challenges posed by dengue fever, a comprehensive approach that encompasses prevention, early detection, and supportive care remains key in mitigating the impact of this widespread and often debilitating mosquito-borne illness.


